At MS Level 1, you plan long-term demand for parts that are manufactured or purchased. When Level 1 is calculated, master schedule proposals create shop order requisitions or production schedules and/or purchase requisitions and/or supplier schedules and/or distribution orders. MRP breaks down only semi-manufactured and purchased components. The parts processed in MS on level 1 do not generate supplies during MRP (unless specifically set to create supplies during MRP for actual demands of MS parts). These supplies are then broken down and then generate a demand of semi-manufactured and purchased components by MRP.
The parts on Level 1 are usually manufactured, although they can also be purchased. These can be considered as the end items as they are at the leaf nodes of planning structures. The topmost part of the planning structure is a Level 0 part. The subsequent parts are Level 0 phantom parts. The bottommost parts of a planning structure (end items/leaf nodes) are Level 1 parts. Level 0 parts and Level 0 phantom parts are used as a concept for grouping in sales and operation planning and subsequently in the Master Production Scheduling process. Forecast information comes to Level 1 from Level 0 once Level 0 forecasts (highest level of planning) are disaggregated i.e., broken down to generate Level 1 forecasts. You can add other forecasts for these parts in Level 1 such as manual forecasts, imported forecasts from demand planning and from customer schedules. A part does not need to have a Level 0 to be planned in MS Level 1.
In a situation where parts are mainly defined as end products in some structures and as components in several other structures, such parts will have dependent and independent demands due to its nature of how it is defined in the structure. If such Component parts are planned by MS or defined as MS level 1 parts, the Supply proposals for parent parts created by MS are broken down and they explode demands to these MS planned Components. These exploded parent MS receipts are visible as Planned dependent demands. During MS level 1 calculation demand explosion stops when it hits MRP planned component.
Master scheduling also supports the concept of multi-site planning through the use of material transfers executed via distribution orders. Multi-site planning can be used when two or more sites interact in a single supply chain, with parts distributed to one or more demand sites from a single supplying site. Multi-site planned parts are defined as supplied from an internal supplier corresponding to the supplying site. You can perform master scheduling for a single site, or alternatively execute master scheduling for multiple sites in support of a multi-site supply chain environment. Master scheduled parts supplied from another site are defined as multi-site planned in the Supplier for Purchase Part window, indicating that the supply comes from an internal supplying site. Master scheduling plans supply proposals across these sites and generates distribution orders for the material move requirements.
While not as sophisticated as multi-site MRP, multi-site master scheduling consists of two or more sites working together in an integrated supply chain. Unlike planning networks in a multi-site MRP, you can execute master scheduling for sites one at a time, but it is up to you to manually determine the order in which master scheduling is executed, for the sites in the supply chain.
Forecasts for project connected parts can also be planned with MS Level 1. In this instance, along with the other parameters, PNG and PPSA (program, project, subproject and activity) information will be connected and displayed with the part. The MS Level 1 calculation will also be performed in connection with the selected PNG.
Master scheduling supports the process of generating supplier schedules. When using master scheduling in this mode the Demand Time Fence and Planning Time Fence on the MS Level 1 Part window should be set to 0 as supplier schedule template rules are applied. The parameter Create S/P Req should be set as Create S/P Req Entire Horizon.
DOP parts can be administrated by MS Level 1, and generally master scheduled DOP parts should have the parameter Gen Fixed MS in MS Level 1 Part window as Not Create MS Receipt and parameter Create S/P Req in MS Level 1 Part window should be set to Do Not Create S/P Req since the pegged supply order will be created by DOP. By selecting the Allow MRP Explosion for DOP Part check box in MS Level 1 Part window, MRP will explode through the default manufacturing structure and create proposals for non-DOP parts in the structure, based on netted MS proposals.
When the parameter Create S/P Req in MS Level 1 Part window is set to Create S/P from MRP, then MRP will create component supplies based on netted MS proposals while MS Level 1 part supply proposals will be created by MRP based on actual demand. Since MRP creates supplies for actual demand the purpose of planning time fence is redundant. Therefore when MRP creates supplies for MS handled actual demand, both demand and planning time fences can be set to an equal value.
MS level 1 calculation can be performed by Integrating with CRP. When performing MS level 1 calculation alone, it considers Site manufacturing calendar. Therefore Shop order requisitions generated by the process will have start date calculated based on site manufacturing calendar.
When MS is performed integrating with CRP, Shop order requisitions generated by MS will be backward scheduled and the start date of shop order requisitions are calculated considering the relevant Work centers / resources and Work center connected calendar availability. In this way more accurate results can be achieved
After Performing MS level 1 , MRP process can be started which plans supplies for lower level components.
MS level 1 will be considering future expiration stocks of an inventory parts if the Mandatory Expiration Date flag is checked for the part and it plans sub MS receipts accordingly.
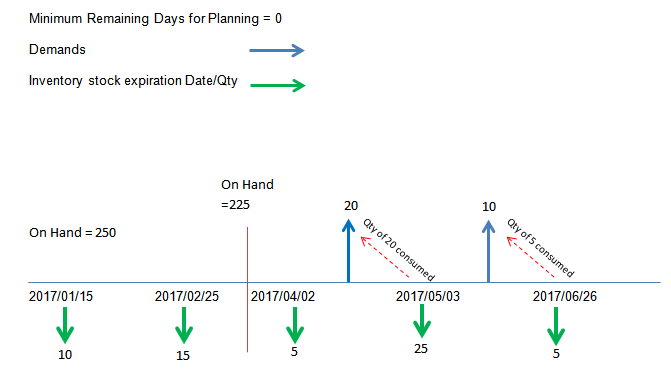
During MS level1 execution, MS level 1 calculates beginning on hand reducing all the expired qty up to system date. This will further be affected if Minimum Remaining Days for Planning is defined for the part in acquisition tab in inventory part.
Before inventory stock get expired it will be consumed by demands fall before the expiration date. This is also affected by the Minimum Remaining Days for Planning, if such stock is remaining even after consumed by demands, the remaining qty will be expired and will be visible in IFS application.

On hand Qty available at the MS level 1 execution date = 250-10-15
Inventory stock Expiration exists on 2017/04/02 for a qty of 5
Inventory stock Expiration exists on 2017/05/03 for a qty of 5 (qty of 20 will be consumed by the demand which exists before the expiration)
Inventory stock going to be expired on 2017/06/26 for a qty of 5 (full qty will be consumed by the demand which exists before the expiration).
The lot expirations are visible in MRP part information for the parts planned by MS. MRP source for such demands will be MRP Inventory Lot Expiration